What Are Calories and Macros?
And Why Do They Matter?
Two of the most important concepts to understand are calories and macronutrients, often referred to as “macros.” These are the foundation of how the body uses food for energy, performance, and overall health.

Author: Helen Conway
Nutritionist
With so much information available about nutrition, it’s easy to feel confused about the basics. Two of the most important concepts to understand are calories and macronutrients, often referred to as “macros.” These are the foundation of how the body uses food for energy, performance, and overall health.
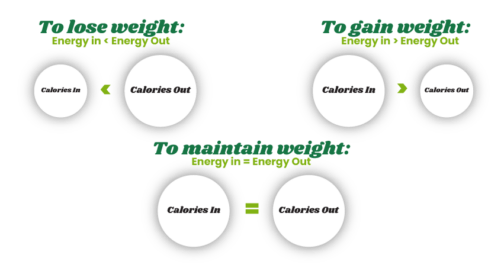
Calories are simply units of energy. The body requires energy to function, not just for exercise, but also for essential processes like breathing, digestion, circulation, and even regulating body temperature. The energy provided by food is measured in calories, and our bodies need this energy to survive. When more calories are consumed than the body needs, it can result in excess storage of fat. On the other hand, when fewer calories are consumed than required, the body resorts to using stored energy, which can lead to weight loss. This energy balance plays a central role in weight management.
However, calories are only one part of the picture. The source of those calories, which comes in the form of macronutrients, significantly influences how the body performs and feels. There are three main macronutrients: protein, carbohydrates, and fat. Each one serves a distinct function and contributes to the total calorie content of food.
Protein is responsible for building and repairing tissues, including muscle. It also supports immune function and helps regulate hormones and enzymes. Common sources of protein include poultry, meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based proteins such as tofu and tempeh. Protein provides 4 calories per gram. It also helps with satiety, making meals more satisfying and keeping you full for longer.
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are especially important for fueling the brain and muscles, particularly during physical activity. Carbohydrates are found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, and dairy. Like protein, carbohydrates provide 4 calories per gram. Choosing complex carbohydrates such as whole grains and fibre-rich foods offers longer-lasting energy and more nutritional value than refined or sugary options. This is because the body finds complex carbohydrates harder to break down, meaning the nutrients are digested and absorbed at a slower rate.
Fats play a key role in supporting brain health, hormone production, and the absorption of certain vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Healthy sources of fat include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and oily fish like salmon. Fat is more energy-dense than the other macronutrients, providing 9 calories per gram, which is why portion control is important. Despite common misconceptions, fat is an essential part of a balanced diet – just make sure to primarily choose healthy fats over greasy or fried foods.
Understanding the relationship between calories and macronutrients helps create a solid foundation for healthy eating. While all three macronutrients are essential, the right balance can vary depending on individual goals and lifestyle.
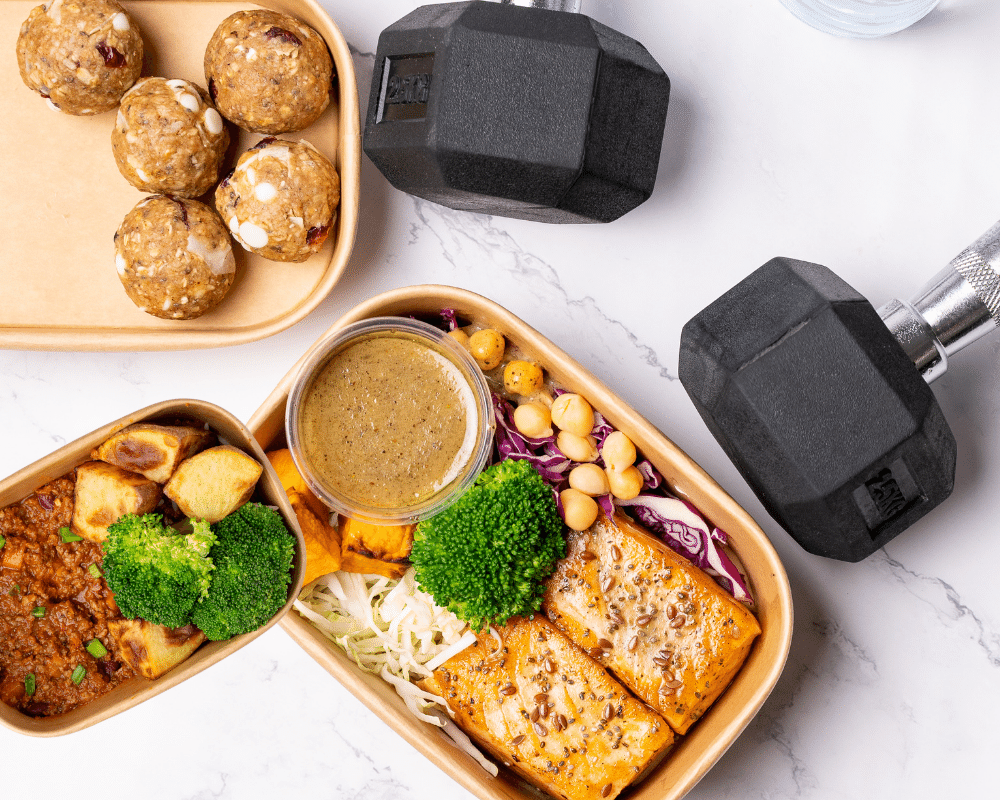
Our FITT meals are designed with this balance in mind, offering macro-controlled, portion-conscious meals that support energy, recovery, and overall wellbeing. With properly balanced meals, it’s easier to stay on track, meet nutrition goals, and feel your best – without the need to measure or guess.





